We’ve all heard the phrase saying, ‘accidents happen.’ In reality, accidents do happen, and sometimes, they can have serious consequences for our teeth. The good news is that dental trauma can be prevented if you know what precautions to take and what to do in case you suffer any damage to your teeth.
What is Dental Trauma
Dental trauma refers to the injury to the mouth area, including the teeth, lips, gums, tongue, and jawbones. While soft tissue injuries on the mouth and dental trauma often result in pain, it is imperative to receive prompt medical treatment. The most common dental trauma is a broken tooth.
Excessive teeth grinding, biting hard foods, slips and falls, and blows during sports injuries can result in dental trauma. While some of the lesser severe dental injuries involve toothaches, broken braces, caught objects between teeth, and bleeding gums.
Dental trauma can happen at any age range. In some cases, the person may not see any scratches or bleeding in the mouth but may experience pain in the gum and jaw area.
Signs and Symptoms of Dental Trauma
- bleeding from the mouth, lips, tongue, or in the tooth socket
- pain around the mouth area following an injury
- a broken or displaced tooth
- swelling in the mouth or around the jaw area
First Aid for Dental Emergencies
Assess the person and the injury
The first thing to do is to assess the situation and determine how serious it is. Check the person to decide whether the injury needs emergency medical attention.
If the injury has affected a large portion of the mouth or facial area, seek professional emergency help right away. This also applies if there is heavy bleeding involved or if the victim is rendered unconscious.
Provide reassurance
The injured person may be quite shaken up after the event, especially when there is serious bleeding. Provide comfort and reassure the person that everything will be okay. Remaining calm will help you take better care of the person during the process.
Recover
Broken teeth that have been chipped in an injury can be recovered. Picking them up also minimises the risk of the person accidentally swallowing them. Place it in milk or inside a small solid container if possible. Make sure to keep your tooth away from water.
Once recovered, you can show it to the dentist, later on, to see if it can be bonded back.
Stop the Bleeding
Heavy bleeding often comes with oral mouth injuries. To stop the bleeding, apply clean gauze to the injury site. Assist the victim as he gently bites down to secure the gauze in place. Alternatively, you can use bags of black tea leaves to help in slowing down the bleeding.
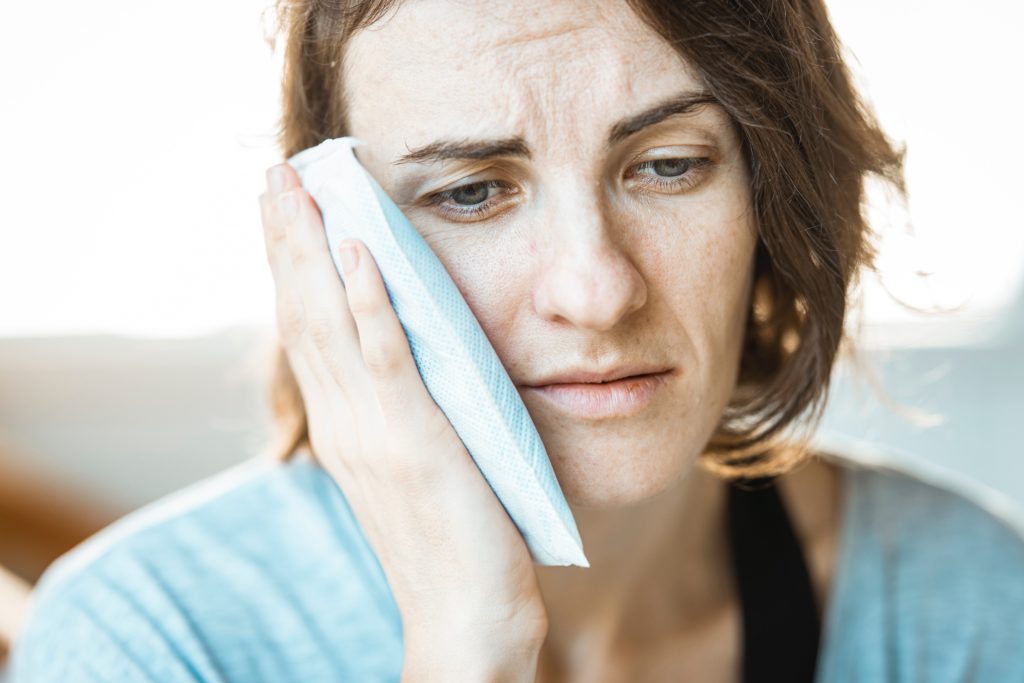
Pain Treatment
The injured person may need to take medications, such as paracetamol, to help deal with the pain. Make sure to take painkillers that are safe and approved by the doctor. A cold towel or an ice pack applied on the outside of the face is also a good way to numb discomfort.
Get medical care immediately if a permanent tooth has been knocked out. It is still best to go see a dentist or emergency room after following the first aid steps above.
In the meantime, rinse your mouth with salty water and use OTC medications for pain relief. If swelling and extreme pain are present, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
To know more about first aid for dental trauma and other medical emergencies, you can always book a first aid training course with us.